5G Network Slice Based Security pptx: A Complete Guide and File
5G technology is transforming connectivity, but it also introduces complex security challenges. One of the most important innovations in 5G is network slicing—the ability to create multiple virtual networks on a shared physical infrastructure. While this allows unparalleled flexibility and performance, it also demands robust, slice-specific security mechanisms.
In this article, we explore 5G network slicing, its security implications, and best practices to protect each slice from threats. This guide can be used to build a compelling PowerPoint presentation or an executive summary for security planning.
📌 What Is Network Slicing in 5G?
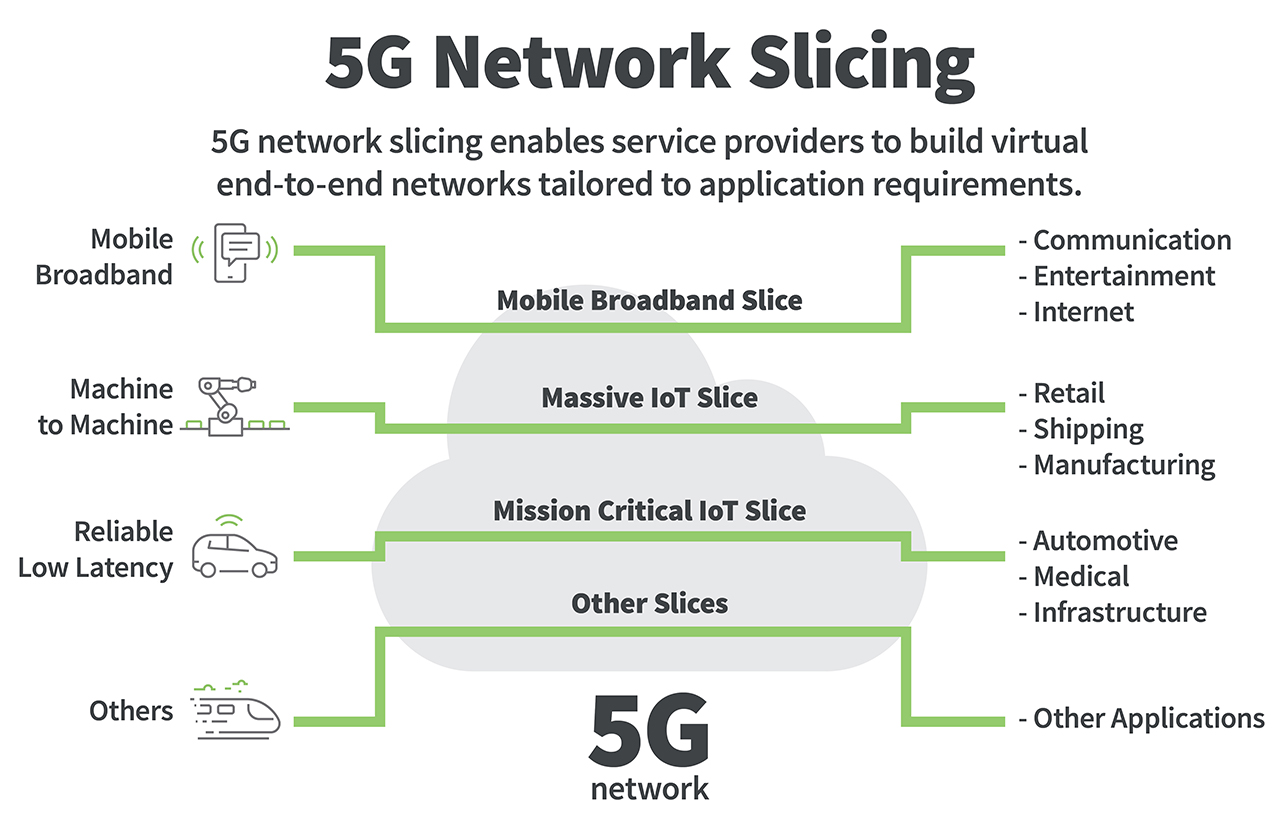
Network slicing refers to creating multiple logical networks (slices) on top of a single physical 5G infrastructure. Each slice is customized for specific use cases:
| Slice Type | Use Case |
|---|---|
| eMBB (Enhanced Mobile BB) | Video streaming, AR/VR |
| URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency) | Autonomous vehicles, remote surgery |
| mMTC (Massive Machine Type Comm) | IoT, smart meters |
Each of these slices operates like a separate network, even though they share the same physical hardware.
🚨 Why Is Security in 5G Slicing So Important?
With slicing, each virtual network handles different levels of data sensitivity, latency, and bandwidth. A breach in one slice can compromise the security of others if isolation isn’t enforced properly.
Key concerns:
- Lateral movement attacks between slices
- Slice hijacking or impersonation
- Data leakage or interception
- Dynamic and complex attack surfaces
🧱 Core Security Principles for Network Slicing
To ensure secure slicing, the following principles must be implemented:
- Isolation: Strict separation between slices (compute, storage, control)
- Authentication & Authorization: Verify entities accessing each slice
- Encryption: End-to-end encryption across slice-specific traffic
- Monitoring: Continuous threat detection per slice
- Policy Enforcement: Slice-specific policies and compliance controls
🔐 Security Architecture in 5G Network Slicing
Here’s how security is integrated into the 5G sliced network:
1. Security at the Management Plane
- Slice orchestration security
- Secure API access (OAuth 2.0, TLS)
- Zero-trust access for slice controllers
2. Security at the Control Plane
- Protect signaling interfaces (e.g., N2, N4, N6)
- Slice-specific authentication and access tokens
- Identity federation and multi-domain access controls
3. Security at the User Plane
- Encrypt data traffic within and across slices
- Packet inspection without violating tenant data privacy
- DDoS mitigation tailored to each slice’s risk profile
📊 Security Lifecycle in Network Slicing (For PPTX Slide)
- Slice Design
→ Define threat model per slice - Slice Provisioning
→ Automate with secure SDN/NFV practices - Slice Operation
→ Real-time monitoring, anomaly detection - Slice Decommissioning
→ Wipe credentials, logs, and policies
🛡️ Use Case: Securing URLLC Slice for Autonomous Vehicles
Imagine a slice dedicated to self-driving cars. It requires:
- Ultra-low latency
- High reliability
- Absolute isolation from other slices
Security Actions:
- Dedicated firewalls and IDS for the URLLC slice
- End-to-end encryption using 256-bit AES
- Slice-specific DDoS filtering rules
Without strict controls, attackers could inject false data or delay communications—causing real-world accidents.
🛡️ Use Case: Securing mMTC Slice for Smart Cities
A slice handling millions of IoT devices (cameras, sensors, meters) needs:
- Massive scale
- Low data rate tolerance
- Strong identity management
Security Actions:
- Use IoT-specific lightweight encryption
- Employ device attestation at scale
- Enforce slice-aware traffic shaping
💡 Best Practices for 5G Slice-Based Security (Slide Material)
- ✅ Implement slice-specific firewalls and IDS
- ✅ Use zero-trust access controls
- ✅ Maintain real-time slice monitoring dashboards
- ✅ Ensure compliance logging for each slice
- ✅ Automate threat response with AI/ML
🔧 Tools & Technologies Supporting Slice Security
- 3GPP TS 33.501: Standard for 5G security architecture
- ONAP (Open Network Automation Platform): For secure slice lifecycle automation
- Kubernetes + Istio: Secure microservices and APIs
- SDN Controllers: Allow dynamic security policy enforcement
🌐 Challenges in Slice Security
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Inter-slice traffic leakage | Enforce strict virtualization boundaries |
| Tenant isolation issues | Harden APIs and apply RBAC |
| Compliance across slices | Enable per-slice audit logs |
| Threat detection gaps | Use AI-based anomaly detection |
🧠 Conclusion
As 5G continues to scale, network slicing security becomes a non-negotiable element in mobile network operations. Whether for mission-critical URLLC apps or IoT-heavy mMTC environments, each slice must be secured individually, monitored in real time, and aligned with global standards.
🎯 A single breach in one slice could endanger the whole 5G infrastructure. Don’t let the flexibility of slicing come at the cost of security.
- Understanding Erome: The Rise of User Generated Adult Platforms

- 5G Network Slice Based Security pptx: A Complete Guide and File

- How Many Cigarettes in a Pack? (Full U.S. Guide on Packs, Cartons, Pricing & Nicotine)

- Best Goth Chick Prompts (and Answers) for Dating Apps: Dark, Witty & Magnetic

- The Grandest Game Summary: What You Need to Know About the Cricket Spectacle